What is Fast Reroute (FRR) in an MPLS network?
In an MPLS network with Segment Routing (SR), ensuring rapid recovery from link or node failures is crucial for maintaining high network availability. Cisco’s IOS-XR supports various Fast Reroute (FRR) mechanisms within MPLS Segment Routing environments, including Link Protection, Node Protection, and Topology Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA). This article will provide a configuration guide and explanations for these MPLS-SR FRR mechanisms in an MPLS SR-enabled network running OSPF as the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP).
What is TI-LFA in an MPLS network?
TI-LFA (Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate) is a fast reroute (FRR) mechanism in MPLS Segment Routing (MPLS-SR) designed to provide sub-50ms recovery from link or node failures in IP/MPLS networks. Unlike traditional LFA, which relies on specific topological conditions and may not cover all failure scenarios, TI-LFA is “topology-independent,” meaning it ensures protection for all traffic flows regardless of network topology. TI-LFA works by precomputing backup paths based on Segment Routing (SR) policies, allowing traffic to be quickly rerouted through alternate paths without complex recalculations. In the event of a failure, traffic is redirected via pre-established repair paths that adhere to the shortest path routing principles (SPF), minimizing packet loss and maintaining high availability across the network.
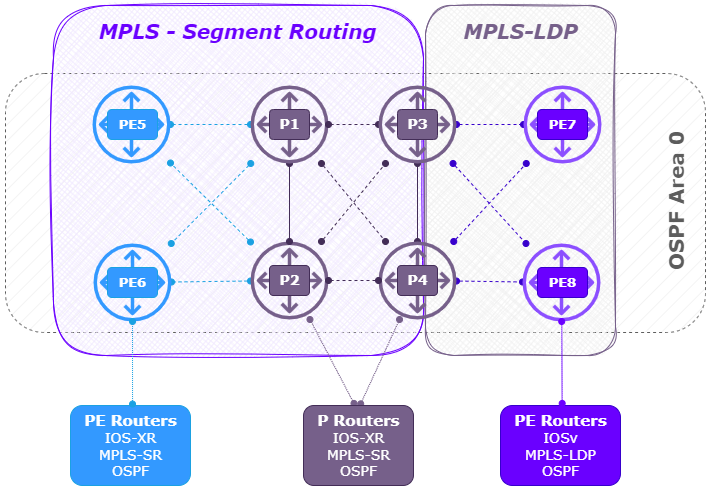
MPLS-SR Lab Setup (Baseline)
Labs download |
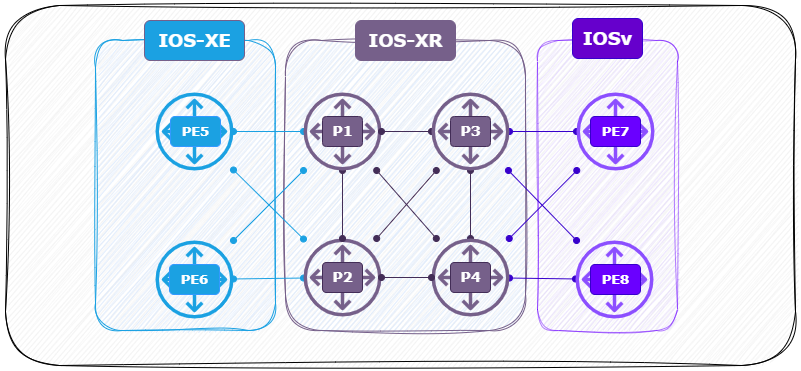
Using Cisco’s Modeling Labs (CML) I build the following MPLS-SR lab using OSPF as the IGP.
- 2 x PE router ( Left ) (PE5, PE6) running XRv with IOS-XR.
- 4 x P router ( Center ) (P1, P2, P3, P4) running XRv with IOS-XR.
- 2 x PE router ( Right ) (PE7, PE8) running IOSv with IOS.
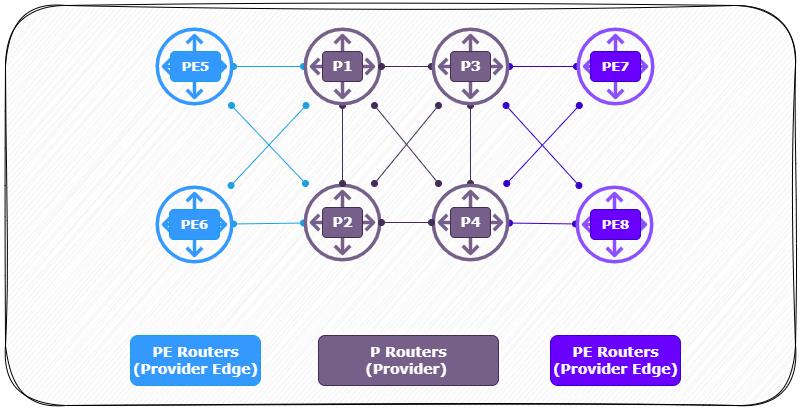
Logical View:
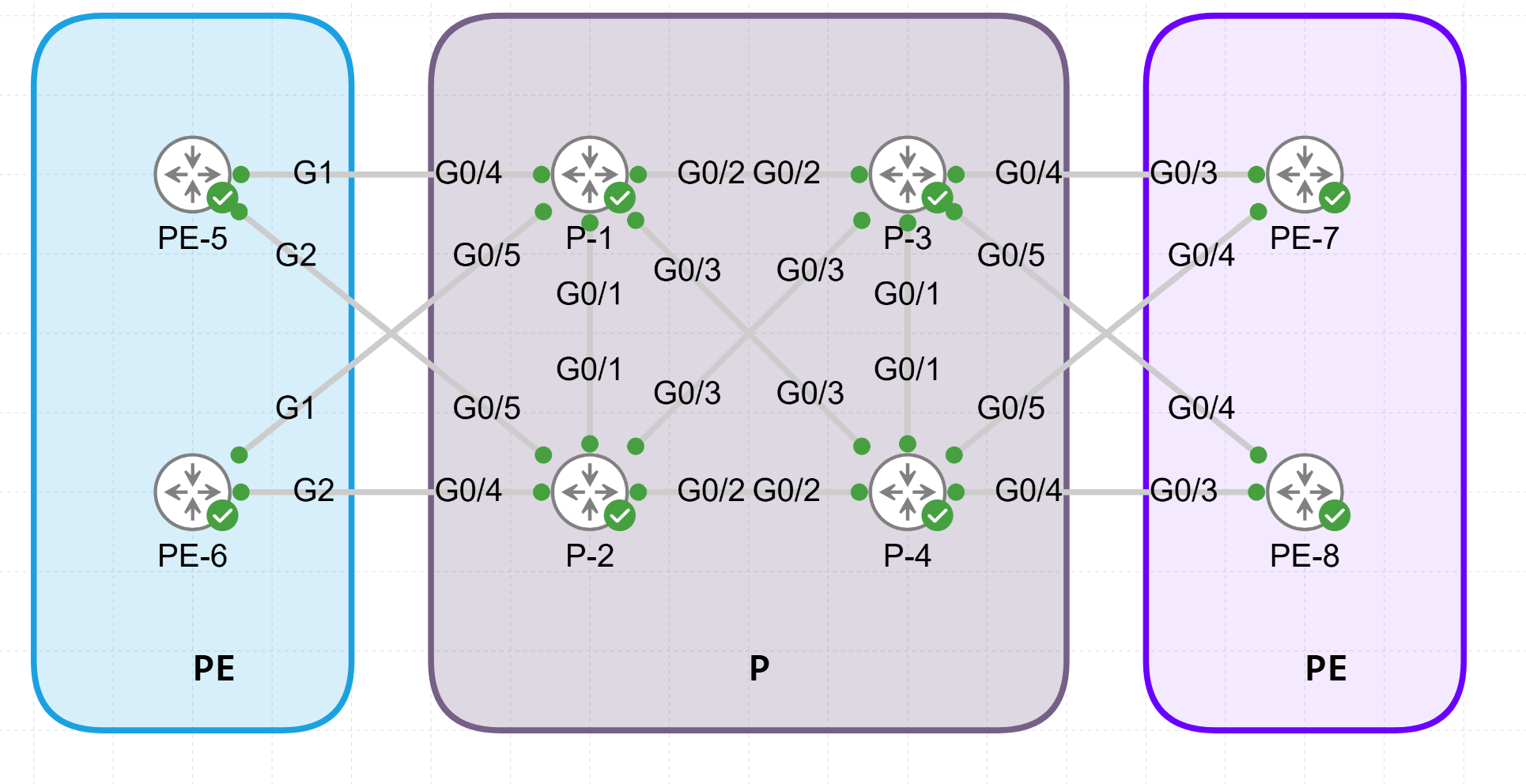
Interfaces: