Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS)
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) is a dynamic link-state routing protocol widely used in large-scale networks, especially in service provider environments. In this post I will look at the following IS-IS configurations;
- Redistribution of OSPF into IS-IS, and the differences between L1 and L2.
- IS-IS Path selection when L1 and L2 routes are available.
- How and where to apply IS-IS Route Summarization.
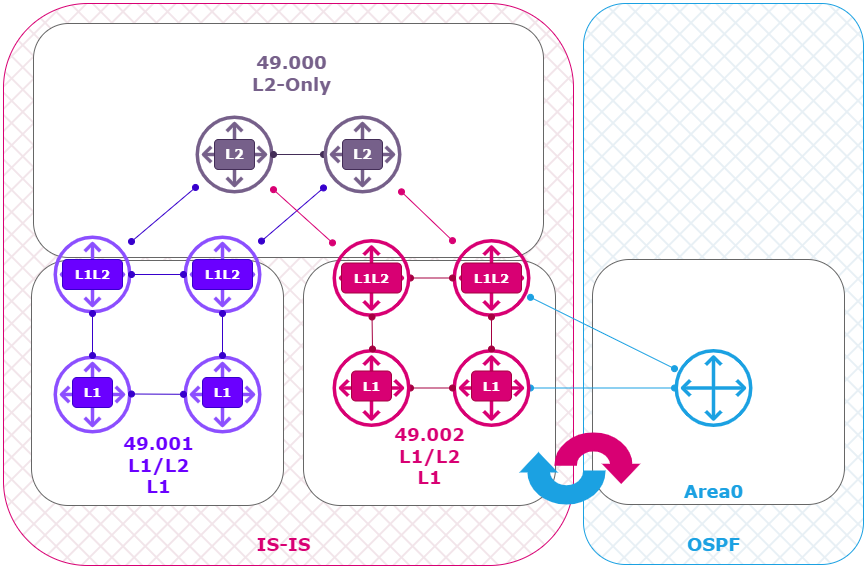
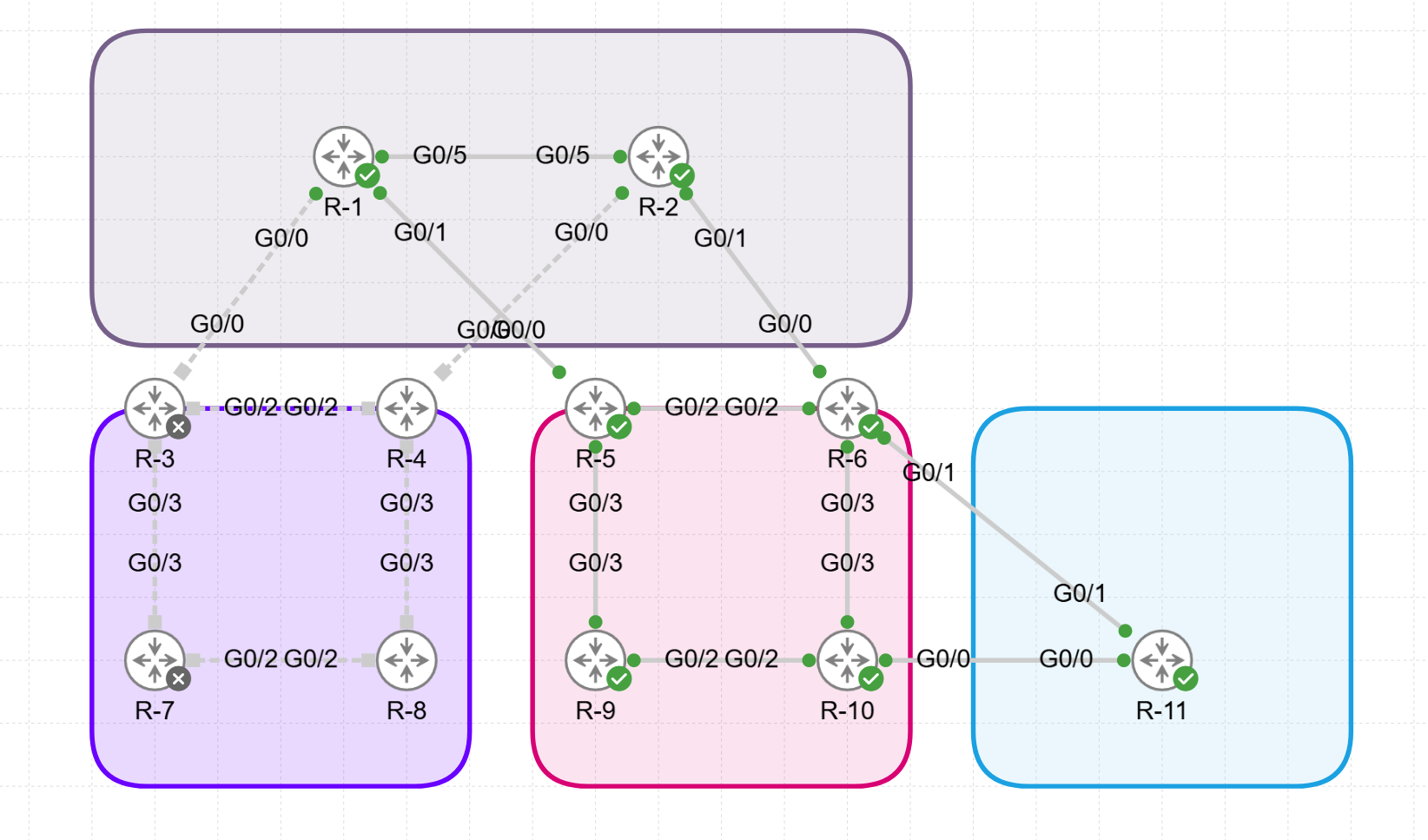
IS-IS Lab Setup
Labs download |
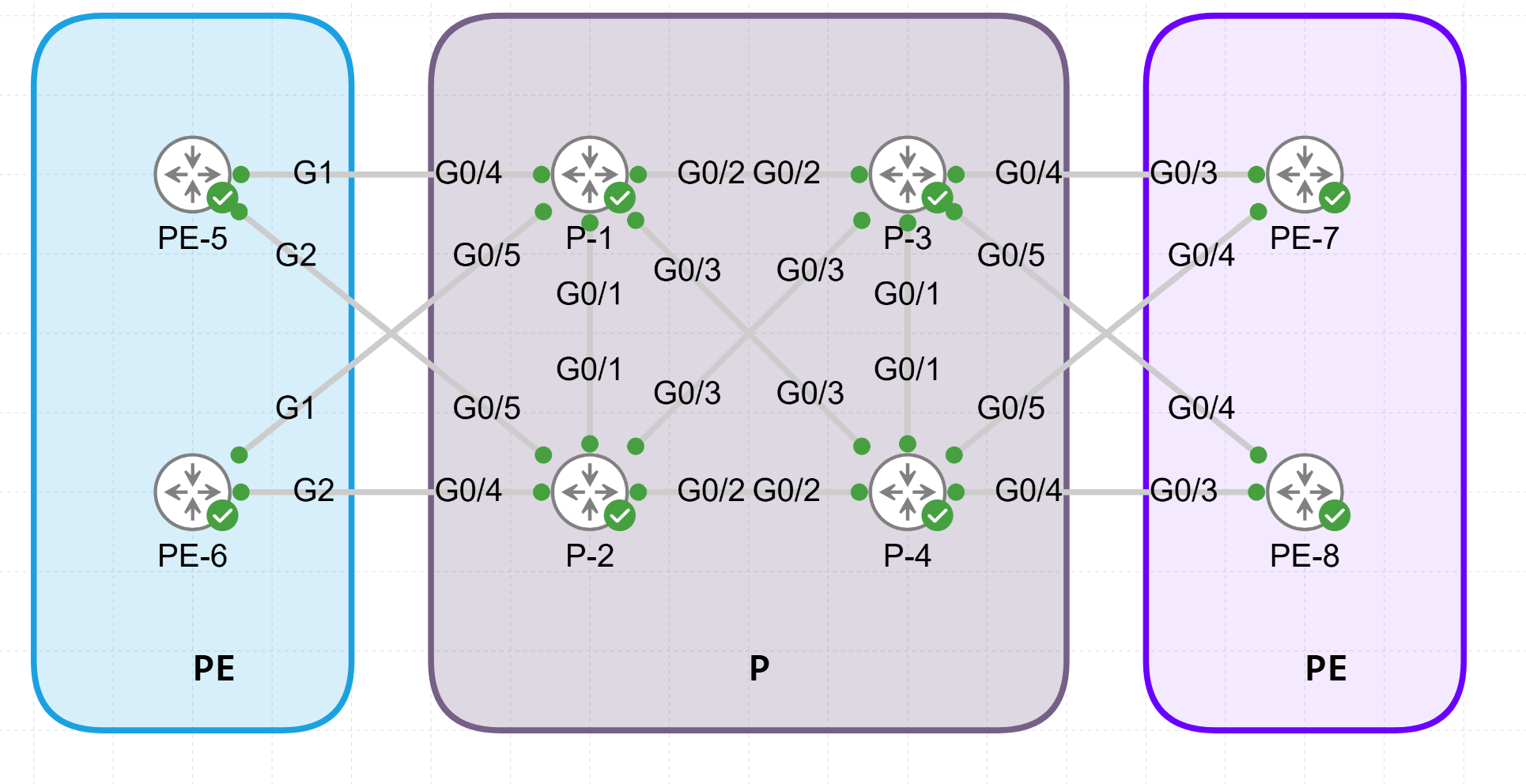
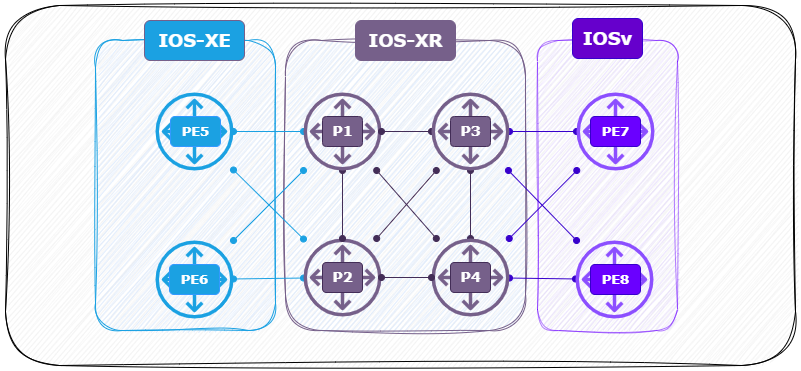
Using Cisco’s Modeling Labs (CML) I build the following IS-IS and OSPF topology:
- 2 x L2 Router ( Top ) (R1, R2) running XRv with IOS-XR.
- 2 x L1L2 Router ( left ) (R3, R4) running XRv with IOS-XR.
- 2 x L1 Router ( left ) (R7, R8) running IOS with IOSv.
- 2 x L1L2 Router ( Center ) (R5, R6) running XRv with IOS-XR.
- 2 x L1 Router ( Center ) (R9, R10) running IOS with IOSv.
- 1 x OSPF Router (R11) running IOS with IOSv.
Logical View:
Physical View: